Daily interactions mean a lot but at the same time it can be challenging for autistic (autism spectrum disorder) individuals, specifically when it comes to developing and applying social skills. These challenges affect their ability to interact effectively with friends and family, resulting in social isolation or sometimes misunderstandings.
As per research, it has been shown that targeted interventions like SST (Social Skills Training) can improve the condition.
So through this blog, we will understand the practical methods for improving social skills and ensuring safety in daily interactions.
What are Social Skills & Strategies in Autism for Daily Interactions?
Most of the time individuals with autism spectrum disorder face challenges in social communication which can impact their ability to interact.
These difficulties arise from differences in processing social cues, understanding nonverbal communication, and interpreting social norms.
Here are some methods to enhance social skills in daily interactions:-
- SST (Social Skills Training) – These are a set of programs that teaches autistic individuals how to engage in social interactions, and how to develop appropriate responses.
- Social Stories – Individualized stories that represent social situations and adequate responses to manage complicated social scenarios for individuals with ASD.
- Peer-Based-Intervention – This program helps peers to facilitate social interactions, models for appropriate behaviours, and support overall social engagement.
- Training for Parents – Preparing parents with strategies to support social skill development at home and in the community to manage consistency and learning behaviours.
- Technology Intervention – Here, tools like virtual reality or mobile applications to stimulate social scenarios, which allows practice for social skills in a safe and controlled setting.
Let’s take an example, a 12 year old autistic boy who finds difficulties in maintaining eye contact during conversations and frequently interrupts others. With the help of a social skills training program, he learned to maintain eye contact, proper conversations, and listen actively.
- Here, the program uses role playing scenarios with both peers and adults with a “conversation chart” that represents when it’s his chance to speak.
- After some time, he feels more confident in social interactions and enhances his ability to engage in conversations, which results in better social connections and a good sense of belonging.
Building the Foundation of Social Skills for Individuals with Autism
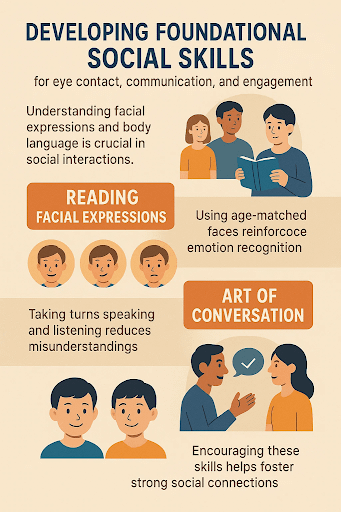
Developing foundational social skills is important for improving daily interactions and supporting meaningful relationships where eye contact plays a major role for social communication, and engagement.
Here are some three basic fundamentals to consider:-
- Understanding Facial Expression
- Here, understanding of facial expressions and body language is essential for clarifying emotions and intentions in social interactions.
- Visual representation, playing role, and real life storytelling to enhance understanding and application of these skills.
- Adequate communion includes not only just speaking but also listening and responding effectively.
- The program involves activities where people take chances for speaking and listening.
- By encouraging these skills, we can support individuals with autism in building powerful social connections and enhance overall quality of life.
2. Reading facial expressions
We can understand this more better with an example – Teaching material like age matched faces has been found to be more beneficial in enhancing the ability of emotion recognition in children with autism compared with use of faces of different ages.
3. Art of Conversation
- Taking turns in conversations is essential for balanced communication to support in learning when to speak and when to listen which reduces misunderstanding.
- Effective listening of not just words but also nonverbal hints like tone and body language. As per research, individuals with autism need help in offering feedback to listeners, as nodding, or acknowledging.
- Understanding context and providing relevant information requires adequate responses in the conversation.
Intervention aims on taking-turn, listening properly, and responding helps to improve communication skills and leads to better social relationships.
Safety in Social Interactions for Individuals with Autism
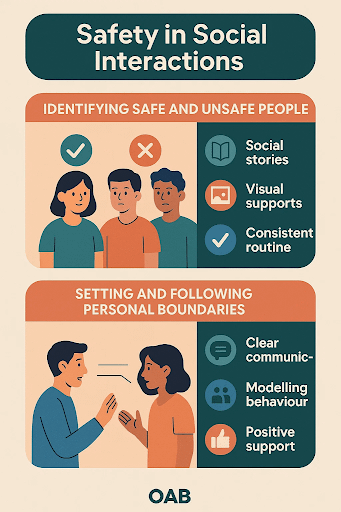
Skills for safety while social interactions are crucial for encouraging independence in daily life. According to research, children with autism find difficulties in identifying safe people and situations, which can increase vulnerability to exploitation and harm.
Here are some points to understand:-
- Identifying safe and unsafe people around – Consistent routines and familiar environment can decrease anxiety and enhance ability to impose safety in social context. As autistic individuals face challenges with spatial awareness and recognition of others, comfort zones can lead to violation of boundaries unintentionally.
Methods:
- Social stories – Visual supports – Consistent routine
2. Setting and following personal boundaries – Practicing situations which involve consent to confirm understanding and application.
Methods:
- Clear communication – Modelling behaviour – Positive support
Tools for Enhancing Social Skills in Autism
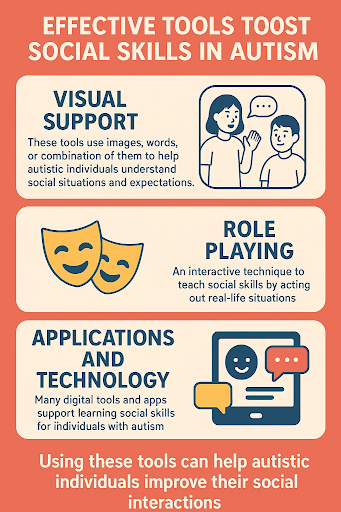
| Visual Support (Social Stories, and Scripts) | Role Playing | Applications and Technology |
|---|---|---|
| | | |
With the help of these combinations of tools, we can help autistic individuals to improve their social interactions.
Summing Up..
- For the engagement of meaningful conversation with others, social skills are important for autistic individuals to avoid feelings of isolation.
- Tools like SST, social stories, and playing-role can help in the fundamentals of taking turns and proper listening.
- With the help of strategies given above, we can enhance the social interactions in individuals with autism.
Curious about understanding more about social skills for your child? Follow Rachna Sawhney Pargi Journey for Autistic Child Support
“Every thoughts is an experiment” This was mine —
Written by Prachi – July,2025
Reference
- Kaur, Ramandeep. 2025. “Interactive Social Pragmatic Intervention and Responsive Engagement (INSPIRE): An Intervention Program to Facilitate Social Skills among Toddlers with Autism.” MethodsX 14 (June): 103352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2025.103352.
- Lee, Kwangwon, Fatima Godina, and Delaney Pike. 2023. “A Social Turn-Taking, Parent Mediated Learning Intervention for a Young Child with Autism: Findings of a Pilot Telehealth Study.” Early Childhood Education Journal, March. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-023-01467-x.
- Yizengaw, Simegn Sendek. 2021. “Effect of Social Skills Training on Interpersonal Interactions of Children with Autism: An Interventional Research.” International Journal of Developmental Disabilities 68 (6): 858–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/20473869.2021.1902730.
- Soares, Erin E., Kimberly Bausback, Charlotte L. Beard, Megan Higinbotham, Eduard L. Bunge, and Grace W. Gengoux. 2021. “Social Skills Training for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Meta-Analysis of In-Person and Technological Interventions.” Journal of Technology in Behavioral Science 6 (1): 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-020-00177-0.
- Vahid Nejati, Aida Peyvandi, Nasim Nazari, and Fatemeh Abadi. 2024. “The Effectiveness of Social Training in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD): A Systematic Review and Transfer Analysis.” Scientific Reports 14 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-83953-9.
- Wall, Natalie G, Oliver Smith, Linda E Campbell, Carmel Loughland, Mark Wallis, Frans Henskens, and Ulrich Schall. 2021. “E-Technology Social Support Programs for Autistic Children: Can They Work?” World Journal of Psychiatry 11 (12): 1239–46. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i12.1239.
- Kennedy, Daniel P., and Ralph Adolphs. 2014. “Violations of Personal Space by Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder.” Edited by Tiziana Zalla. PLoS ONE 9 (8): e103369. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103369.







No comments yet. Be the first!