
Introduction
Ever found yourself humming the same tune for hours, or perhaps, stuck on a particular topic of all else? These are all regarded as mere quirks and easily dismissed.
But for many, these traits are not just habits– they are the windows of their brain into this beautiful world where the brain processes, perceives, and reacts distinctly.
Welcome to the spectrum of autism! Let us dive into this..
Overview of Autism Spectrum Disorder
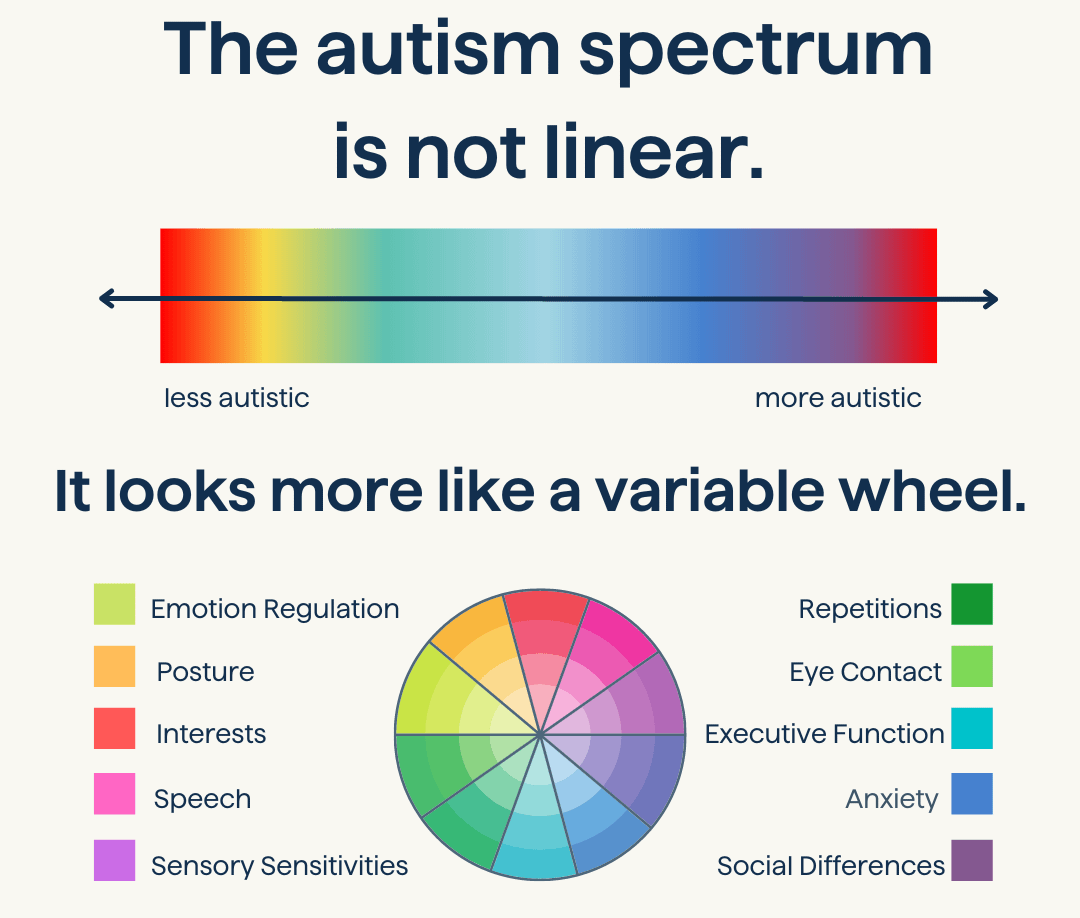
Types of ASD
There are distinctively three different types of Autism Spectrum Disorders:

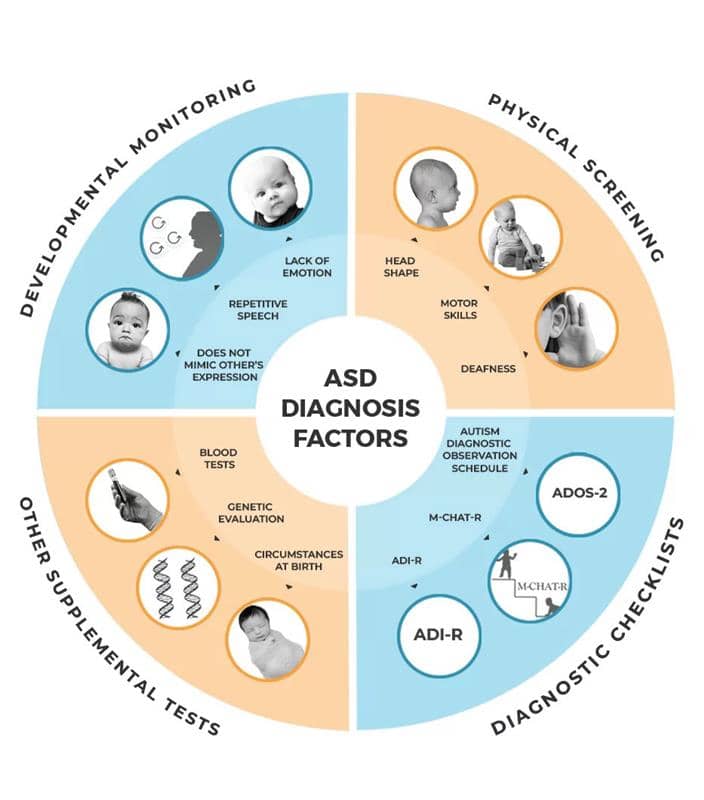
Core characteristics of Autism
The symptoms or the core characters can vary from individual to individual. The symptoms can cause an individual to need help in their daily life.
Some of the characteristics are quite common, others are typical and few are not necessarily experienced by all who are on the autism spectrum.
Strengths as“Being different is a superpower”:
Every superhero has their Kryptonite; and some of our abilities have drawbacks, too!
We will subject the core characteristics or signs- symptoms for two different groups namely Child and Adults.
Child
1. Behavior
2. Communication
3. Cognition

Adults
1. Behavior
2. Communication
2. Cognitions
Lesser- known yet recognizable traits
Beyond all the well- known characteristic features, there are several lesser known traits that have increasingly recognised:
Neurodiversity in Everyday Life: Spot the Similarities
We can actually acknowledge neurodiversity and celebrate the natural variation in the human brain.

Conclusion
Do you know?

What’s Next for You?
Want to learn more about embracing your unique brain?
Stay tuned Rachna Sahney Pargi Journey for Autistic Child Support, for more articles that dive deep into human diversity, mental health, and how to navigate life in a neurodiverse world.
References
- Ghaneshirazi, Zahra. (2018). Autism Spectrum Disorder. (PDF) Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Hodges H, Fealko C, Soares N. Autism spectrum disorder: definition, epidemiology, causes, and clinical evaluation. Transl Pediatr. 2020;9(Suppl 1):S55-S65. doi:10.21037/tp.2019.09.09
- Naji, Wafaa & Qasim Waheeb, Mohammed. (2020). Autism Spectrum Disorder: Review Article. Medico-Legal Update. 20. 324-329. (PDF) Autism Spectrum Disorder: Review Article
- Wikipedia. (n.d.). Autistic Masking. Retrieved from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autistic_masking]
- Adams, J. B., Johansen, L. J., Powell, L. D., Quig, D., & Rubin, R. A. (2011).Gastrointestinal flora and gastrointestinal status in children with autism – comparisons to typical children and correlation with autism severity. BMC Gastroenterology,11(1). doi:10.1186/1471-230x-11-22






No comments yet. Be the first!